Profit plays a pivotal role in the world of business. It is not just a symbol of success but a necessity for the survival and growth of any business entity.
Profit is the financial reward that entrepreneurs receive for the risks they undertake when investing resources into a business venture. It is a critical indicator of the efficiency and effectiveness of business operations.
Profits help businesses expand, create jobs, innovate, and provide services or products to consumers. Without profit, a business cannot sustain operations, invest in future growth, or survive in the competitive marketplace.
Therefore, profit is the lifeblood of business, driving decisions, strategies, and goals.
Definition: Profit
Profit is the financial gain or surplus that results when the revenue generated from a business activity exceeds the expenses, costs, and taxes needed to sustain the activity. It’s essentially the reward for taking a risk and making an investment.
Profit is important to businesses as it impacts their ability to invest, expand, provide returns to shareholders, and create jobs.
Types Of Profit
Here are the details of profit types.
Gross Profit
This is a company’s profit after deducting the costs associated with making and selling its products or the costs associated with providing its services. Gross profit will appear on a company’s income statement and can be calculated by subtracting Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) from Revenue.
Net Profit
Also known as net income or bottom line, net profit is the amount a company has left over after subtracting all its expenses, including operating costs, interest, taxes, and costs associated with non-core business activities, from its total revenue.
It’s the most comprehensive reflection of a company’s profitability.
Operating Profit
Operating profit, also known as operating income or margin, is the profit from a firm’s core business operations, excluding interest and tax deductions. It reflects the profits made from regular business operations, ignoring the impact of financing costs and tax laws, thus providing a more accurate view of the business’s operational efficiency.
How Profit Is Calculated
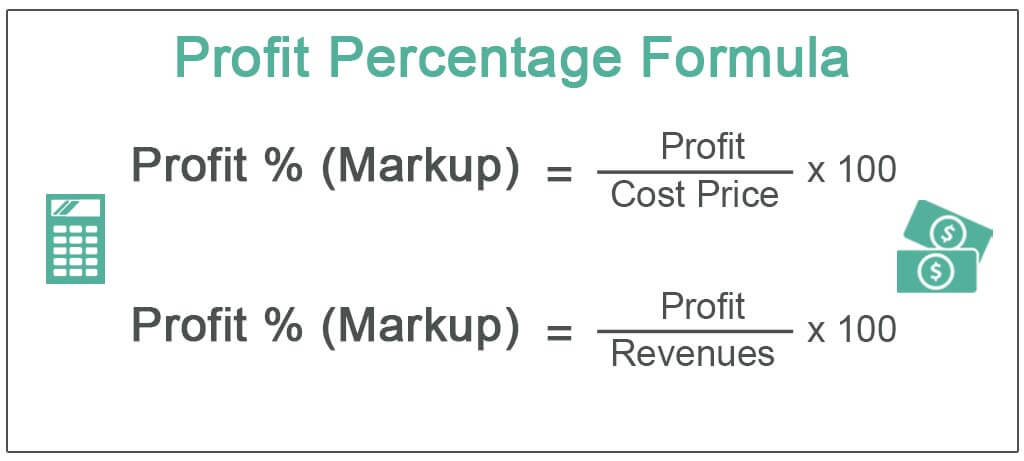
Profit is calculated by subtracting all the various costs and expenses incurred in running a business from the total revenue generated. Here’s a basic outline of how it’s done:
- Calculate Total Revenue: The total income from selling a product or service. It can be calculated by multiplying the product’s price by the quantity sold.
- Calculate Total Costs: These include variable costs (costs that change with the output level, such as raw materials) and fixed costs (costs that do not change with the output level, such as rent and salaries).
- Subtract Total Costs from Total Revenue to get Gross Profit: Gross Profit = Total Revenue – Total Costs
- Subtract Business Operating Expenses from Gross Profit to get Operating Profit: Operating Profit = Gross Profit – Operating Expenses
- Subtract Taxes and Interest from Operating Profit to get Net Profit: Net Profit = Operating Profit – (Interest + Taxes)
Role Of Profit In Business Operations
Profit plays an integral role in the functioning and growth of a business. It’s not just about survival but also about expansion, innovation, and rewarding the people who make the business successful.
Financing Daily Operations
The day-to-day operations of a business require an ongoing influx of funds. From paying for utilities to purchasing inventory, settling bills, and managing payroll, every facet of daily operations is financed by the profit earned by the company.
Without sufficient profit, businesses may struggle to cover these expenses, which could lead to operational inefficiencies or even insolvency.
Reinvestment In Business: Expansion, Innovation, And Upgrades
Profit provides the capital necessary for growth and expansion. Businesses can reinvest their profits into various areas, such as opening new branches, launching new products or services, or upgrading their technology and equipment. By reinvesting profits, businesses can improve their competitive advantage and increase their market share.
Moreover, profit allows businesses to invest in research and development, fostering innovation that can lead to more efficient processes, new product offerings, and, ultimately, higher profitability.
Employee Compensation And Benefits
Profit is also crucial for rewarding and retaining employees. A profitable business can afford to pay competitive salaries, provide comprehensive benefits, and perhaps even offer profit-sharing schemes or bonuses.
This helps attract talented individuals and motivates employees, leading to increased productivity and job satisfaction. In this way, profit contributes to a positive company culture and helps build a dedicated and loyal workforce.
Profit As A Measure Of Success

Profit is often considered a primary measure of success for businesses. It is a tangible indicator of the effectiveness of business strategies and operations. Here’s why:
- Sustainability: Profitability ensures that a business can continue operating and growing. Without profits, a business may struggle to maintain operations or invest in future growth.
- Return on Investment: For business owners and investors, profit is a return on their investment. Higher profits can mean a higher return, making the business more attractive to current owners and potential investors.
- Indicator of Efficiency: Profit margins, calculated by dividing net profit by total revenue, can indicate how efficiently a business operates. A higher profit margin usually means the business manages its costs well relative to its revenue.
- Competitive Advantage: High profitability can give a business a competitive advantage. It may allow the business to invest in new products, services, or technologies that competitors may not afford.
- Resource Allocation: Profits can show a business where its most lucrative areas are. This can help it decide where to allocate resources in the future.
However, while profit is an important measure of success, it’s not the only one. Other factors like customer satisfaction, market share, social and environmental impact, employee satisfaction, and contribution to the community are also important indicators of a business’s overall success.
How Profit Influences Market Competition
Profit plays a pivotal role in influencing market competition. It serves as a driving force for businesses to strive for efficiency and innovation, thus fostering a competitive environment.
One of the ways profit influences market competition is through its impact on the number of sellers in the market. High profitability can attract more firms to the market, intensifying competition. Conversely, low profits might deter potential entrants, reducing competition.
Profit also affects the quality of goods and services. To increase profitability, companies might strive to produce higher quality products or offer superior services to stand out from competitors.
Furthermore, a study found that product market competition positively influences firms’ performance and profitability. This suggests that companies facing stiff competition perform better, leading to higher profits.
Additionally, market share has a significant influence on profitability. Businesses with a larger market share will likely have higher profit margins due to economies of scale and reduced marketing costs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, profit plays a vital role in the business world. It’s a primary measure of success, indicating a company’s efficiency, sustainability, and competitive advantage.
Profit margins, including gross, operating, and net profit margins, are crucial financial metrics that offer insights into a company’s pricing strategy and control over costs.
Moreover, profit is a significant driver of market competition. It influences the number of sellers in the market, the quality of goods and services, and firms’ market share.
High profitability can attract more players to the market, intensifying competition, while low profitability might deter potential entrants.
However, it’s essential to remember that while profit is a critical indicator of business success, it’s not the only one.
Customer satisfaction, employee satisfaction, and social and environmental impact also matter in evaluating a company’s overall performance.


